Development trend of grid-side energy storage
With the implementation of low-carbon policies, global energy storage industry grid-side energy storage has entered a period of rapid development.
According to a report released by the American Clean Power Association (ACP) and consulting firm Wood Mackenzie, the capacity of grid-scale energy storage systems will reach 2,773MW in the second quarter of 2024, with a storage capacity of 9,982MWh, second only to 13,437MWh in the fourth quarter of 2023.
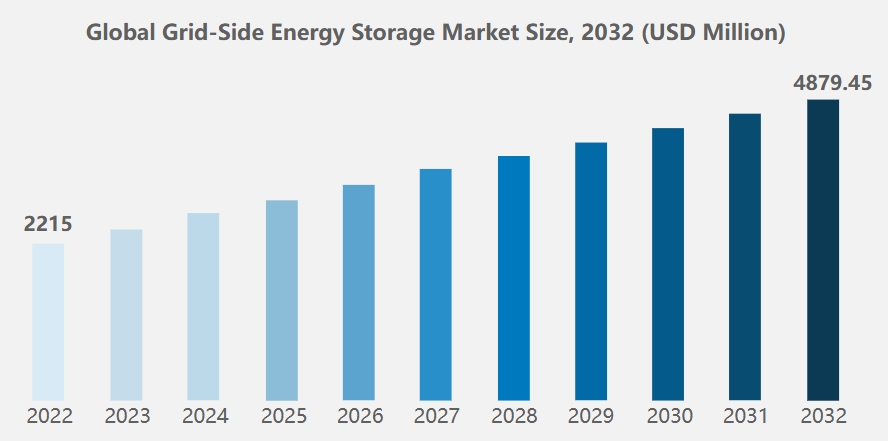
The market size is expected to reach US$4.87945 billion in 2032, with a compound annual growth rate of 8.2%. This shows the rapid development of grid-side energy storage. AEAUTO, as a prominent player industry leader in the energy storage field, is dedicated to capitalizing on this growth momentum and making significant contributions to grid stability and energy optimization energy optimization, which aligns with the long-tail trend of low-carbon and intelligent power development.
Below, AEAUTO will conduct an in-depth analysis of the advantages, applications, and profit models of the energy storage industry on the grid side.
Advantages of grid-side energy storage
- Load balancing: By storing excess energy when demand is low and releasing it when demand is high, this solution helps balance system loads and prevent overloads. This can help reduce the risk of blackouts and other interruptions and improve overall system efficiency.
Take Germany as an example. During its energy transition, Germany frequently encountered intermittent problems with renewable energy generation, resulting in large fluctuations in electricity supply and demand. After the introduction of the grid-side energy storage system, the load fluctuations of the local power grid were effectively smoothed. According to statistics from the German Energy Agency, due to the assistance of energy storage, the average power outage duration in some pilot areas was reduced by 15 – 20 hours per year, and the overall system efficiency was improved by about 8%, which effectively reduced various power supply problems caused by imbalances in supply and demand.
- Peak shaving and valley filling: grid-side energy storage can charge during low periods and discharge during peak periods, effectively alleviating the contradiction between power supply and demand and improving the economics of the power system.
The Australian National Electricity Market (NEM) is a typical case. The peak and valley differences in electricity consumption in this market are obvious. There is a huge difference between the peak electricity consumption for cooling in summer and the trough electricity consumption at night. After the local large-scale deployment of grid-side energy storage equipment, through accurate charge and discharge scheduling, the power supply pressure during peak hours is reduced by about 20% every year, the off-peak power utilization rate is increased by more than 30%, and the operating costs of the power system are reduced by about 12%, significantly alleviating The contradiction between supply and demand is eliminated, and the economic benefits are considerable.
- Optimize resource allocation: By storing electric energy, grid-side energy storage can help optimize resource allocation, realize remote transmission and sharing of electricity, reduce line losses, and improve the operating efficiency of the power system.
Denmark is committed to building a green energy island. The island has abundant wind power resources, but there is a geographical distance between the power generation site and the power consumption area. After the grid-side energy storage is put into use, electric energy can be stored and allocated efficiently, and the line loss rate during transmission has been reduced from the original 8% to about 3%. The cross-regional sharing of electricity has become smoother, which has greatly improved the operating efficiency of the entire power system and ensured the efficient circulation and rational use of energy.
- Improve power supply reliability: In the event of sudden power accidents or natural disasters,grid-side energy storage can provide emergency power support to ensure continuous power supply to important facilities.
Application scenarios of grid-side energy storage
- Large-scale wind and solar power stations: Deploying grid-side energy storage near large-scale wind power and photovoltaic power stations can effectively alleviate the volatility of renewable energy generation and improve grid connection performance.
For example, in the Mojave Desert area of California, there are many large-scale photovoltaic power stations. Previously, due to the intermittent nature of photovoltaic power generation, grid connection problems were prominent. After the introduction of grid-side energy storage, photovoltaic power can be stored and released on demand, and the abandonment rate of local photovoltaic power stations has dropped sharply from 15% to less than 3%. The stability of wind power grid connection has also been greatly improved, and the standard deviation of wind power fluctuation has been reduced by more than 40%, which has strongly supported the smooth access of new energy power to the grid.
- Urban distribution network: Introducing grid-side energy storage in urban distribution networks can improve power supply reliability and power quality, and meet the needs of high-load, high-density power consumption areas.
Take Singapore as an example. With a dense population and developed commerce, the power load remains high all year round. After the introduction of grid-side energy storage equipment in Singapore’s power grid, power quality problems such as voltage drops and harmonic interference during peak hours were reduced by about 60%, and power supply reliability was improved to 99.99%. Even in extremely hot weather, power outages rarely occur in high-load power consumption areas, fully meeting the city’s complex power demand.
- Power system peak shaving: By deploying grid-side energy storage at key nodes of the power system, rapid peak shaving of the power system can be achieved, improving the efficiency of power operation.
For example, during the peak hours of heating in winter in the UK, electricity demand soars, and traditional thermal power peak shaving has a slow response and high cost. After deploying grid-side energy storage at key nodes, the power system can quickly respond to peak shaving instructions within 1 – 2 minutes, with an additional power supply of 100 – 150 megawatts during peak hours, filling the power gap and reducing peak shaving costs by about 30%, making power operation more flexible and efficient.
- Smart microgrid: Addinggrid-side energy storage to smart microgrids can achieve energy self-sufficiency and surplus power sharing, improving the operating efficiency and stability of microgrids.
For example, in Berlin, Germany, after adding grid-side energy storage, the energy storage system can be flexibly charged and discharged according to real-time load demand and power generation conditions, which improves the overall operating efficiency of the microgrid by about 20%. In terms of surplus power sharing, through intelligent scheduling, excess electricity can be sold to nearby commercial users, which can bring about 5,000 euros of additional income to the microgrid operator every month.
AEAUTO grid-side energy storage profit model
- Compensation for ancillary services: compensation is obtained through peak shaving and frequency regulation, and peak shaving fees are collected by smoothing the load curve through valley charging and peak discharging; frequency stability is maintained through rapid response, and frequency regulation fees are collected based on response indicators.
- Capacity leasing:Leases energy storage capacity to distributed power sources and other entities, allowing them to store surplus electricity and use it when there is a power shortage, and charges leasing fees.
- Demand response compensation: In case of power grid emergency, adjust charging and discharging according to dispatch instructions, provide demand response services, and get financial compensation from the power grid.
- Delaying upgrades to make profits: Alleviating power supply pressure, postponing grid transformation, and obtaining one-time or phased economic returns from the grid. In some European countries, the deployment of grid-side energy storage has alleviated power supply pressure and postponed some grid transformation plans, thereby obtaining one-time or phased economic returns from the grid.

Nanjing AEAUTO grid-side energy storage solution, with advanced energy storage technology and intelligent management and control system, accurately solves the load balance problem of the power system and ensures stable and continuous power supply in all aspects.
AEAUTO helps the sustainable development of the power system and leads the grid-side energy storage to a new journey of higher quality development.
